With the extensive media coverage, the shutting down of almost all major sporting and entertainment events, and the instantaneous social media updates, you are most likely already aware of COVID-19, as well as, the resulting global pandemic. However, with the vast amount of information we are receiving, it is hard to wade through all the facts and highlight what is important during this time of crisis. As such, this is intended to be used as a fact sheet designed to give you all the pertinent information that you need to know about the virus and its effects on health.

So what is NCOV 2019, COVID-19, and SARS-CoV2?
So by now, you have most likely encountered these three terminologies being used to describe the virus causing this pandemic. Initially, the virus was first identified due to an increasing number of cases originating from Wuhan in the province of Hubei in China. From samples obtained from those patients, medical professionals were able to first identify the virus which was found to be of the family Coronaviridae. This is a large group of viruses that are capable of causing respiratory and flu-like symptoms ranging from the common cold to more severe cases. Further research, however, showed that this was a new, previously undetected, strain that was capable of fast and far-reaching contamination, as well as, causing severe respiratory difficulties that may result in death. At the time it was termed as NCOV 2019 or Novel Corona Virus 2019.
As the virus quickly spread throughout China, and soon, reached more countries around the globe, the characteristics and the nature of the virus was more closely studied and monitored. It was then decided by the medical community to properly name the virus which is now being identified as SARS-CoV2 or Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. This terminology gives proper indication to the disease entity, as well as, the specific virus causing it. COVID-19 or Coronavirus Disease 2019 is the term given to the disease that is currently affecting patients, as well as, the global pandemic. Similar to how HIV causes AIDS, SARS-CoV2 is what is causing COVID-19.

How is SARS-CoV2 spread?
Current evidence shows that SARS-CoV2 is mainly spread person-to-person by respiratory droplets. This refers to the droplets released during coughing or sneezing which are capable of traveling for about 6 feet. A person may also be infected if they touch hands, surfaces, or objects that have droplets on them; then proceed to touch their own nose, mouth, or possibly eyes, without washing or properly disinfecting first. During the earlier stages of the growing epidemic, the focus was on limiting contact with those who have recent travel history to affected regions in China, however, in this current pandemic, there is enough evidence that supports community spread or local transmission, meaning, it has now been spreading within groups of people without any travel history. Ethnicity is not a factor of spread. All populations are currently at risk for contracting the illness, regardless of their ethnicity or race.

What are the symptoms of COVID-19?
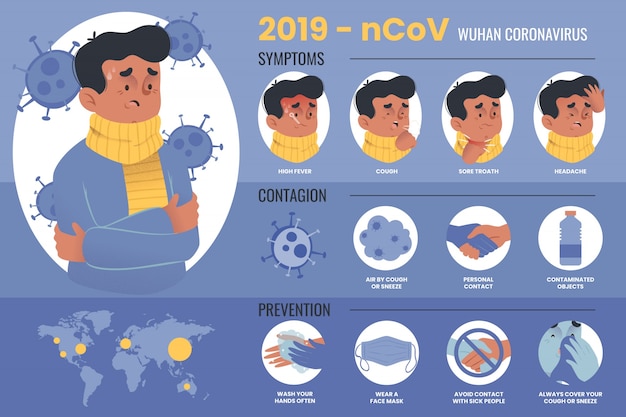
The initial difficulty with COVID-19 is that during the early stages, the disease can present with mild flu-like symptoms which include fever, cough, colds, and shortness of breath. The potential danger, however, is that the illness has been found to be able to quickly develop into a rapid worsening of respiratory functions. This is termed as ARDS or Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. As more of the virus enters through the lungs and the body tries to fight off the infection, it results in more damage which leads to worsening difficulty of breathing. When it reaches this stage, it turns into a medical emergency that may require intubation to allow for better oxygen support, as well as admission into an intensive care unit. The resulting severe respiratory distress may even result in death.
Is it worse than the Flu?
A common phrase and post on social media is to not be worried or alarmed because “it’s not worse than the flu”. This was a commonly held belief during the initial stages, even by some in the medical community, due to the statistics and epidemiologic trends at the time. However, it was too premature to declare that statement and current trends show us something different. While the seasonal flu does affect many Americans every year, with the CDC reporting an average of 8% annually, and also leads to mortality with an average of around 0.1% in the US, there are alarming differences with COVID-19. The first one being that COVID-19 is found to be more infectious than that of the seasonal flu. Based on the current trends, the seasonal flu in the US has an infectivity rate of around 1.3 while SARS-CoV2 has that of roughly around 2-3. This means that one infected person can spread the illness to around 2 or 3 people. Furthermore, the mortality rates, depending on the region and country, now seem to be higher than originally predicted. Upon initial reports from China during the earlier periods, mortality was estimated to around 1.3%-2% depending on the source. Now, globally, accounting for variances between country and region, mortality is roughly around 3-3.5%. It must be taken into consideration that mortality is due to a variety of factors, and not just the disease itself. It is influenced by factors such as the capacity and capability of each region’s healthcare sector and the demographic trend of the population there. A worrying example would be that of Italy. Italy is now one of the hardest-hit countries with its healthcare facilities almost being completely overwhelmed. As such, they also have reported the highest mortality rate with a staggering estimate of around 6%.
One must also remember when comparing the seasonal flu to COVID-19, is that there are vaccines and treatment guidelines that have been well-established and clinically-proven to be effective at managing the seasonal flu. However, COVID-19 presents uncharted waters with no available vaccine and a few studies that show completely effective treatment of the disease.

Is it only dangerous for the old, elderly, and sick?
Another commonly thrown around statement is that COVID-19 is only dangerous if you’re elderly or have an underlying medical condition such as hypertension or diabetes. Yes, the epidemiologic data does show us that the most at-risk population are older and have comorbidities. Current data shows us that the most at-risk age group for mortality are those 80 years old and above. However, the data also shows us that there is an exponential rise in the number of deaths starting at the age of 50. The risk is further compounded if the individual has underlying health issues identified as hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, chronic respiratory disease, and cancer. However, this does not mean that these populations are the only ones capable of being infected or at risk of developing acute respiratory distress syndrome. As mentioned previously, SARS-CoV2 has a high infection rate and is capable of local and community spread. This means, the more people infected, the higher the possibility of the virus reaching the at-risk groups. Furthermore, the more infected, even in the younger age groups, will eventually put a strain on the capacity and capability of the healthcare system and may potentially cause a shortage of both diagnostic test kits and access to medical care for those more at risk.
If you want to know more about how to quarantines, testing, and how to prevent the spread of COVID-19, read more here at BuyMedical.com.

